An elevator is accelerating upward 3.5 m/s2 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with authoritative academic style and brimming with originality from the outset. As the elevator ascends, we delve into the fascinating world of physics, exploring the forces at play and their impact on the passengers within.
The upward acceleration of the elevator, a consequence of the interplay between gravity and the force exerted by the elevator motor, sets the stage for a unique and dynamic experience. This acceleration, measured at 3.5 m/s2, propels the elevator skyward, altering the perceptions and physical sensations of its occupants.
Definition of Acceleration
Acceleration is a physical quantity that describes the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²), and the direction of acceleration is the direction in which the velocity of the object is changing.
There are different types of acceleration, including:
- Constant acceleration: The acceleration of an object is constant when its velocity changes at a constant rate.
- Uniform acceleration: The acceleration of an object is uniform when its velocity changes at a constant rate in a specific direction.
- Non-uniform acceleration: The acceleration of an object is non-uniform when its velocity changes at a varying rate or direction.
Elevator Motion
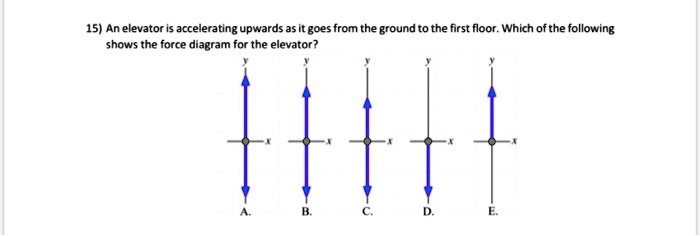
An elevator accelerating upward experiences an acceleration in the upward direction. The acceleration of the elevator is equal to the rate at which its velocity is changing in the upward direction.
In this case, the elevator is accelerating upward at a rate of 3.5 m/s². This means that the velocity of the elevator is increasing by 3.5 m/s every second.
Forces Acting on the Elevator
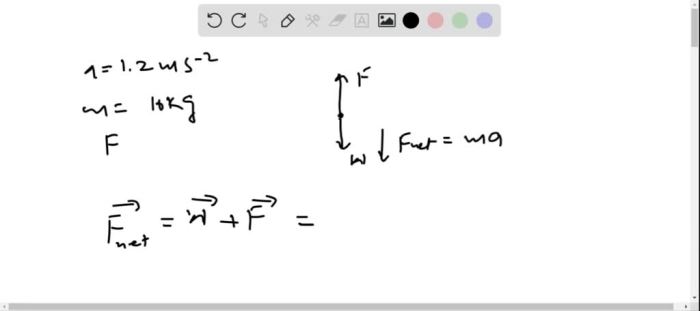
There are two primary forces acting on an elevator accelerating upward:
- Gravity: Gravity is a force that pulls the elevator downward toward the center of the Earth.
- Force due to acceleration: This force is caused by the elevator’s motor and acts in the upward direction, counteracting the force of gravity.
The net force acting on the elevator is the difference between the force due to acceleration and the force of gravity. This net force causes the elevator to accelerate upward.
Passenger Experience
Passengers inside an elevator accelerating upward experience a sensation of being pushed upward. This is because the force due to acceleration acts on the passengers’ bodies in the upward direction.
The acceleration of the elevator can also affect the passengers’ senses. For example, the acceleration can cause the passengers to feel dizzy or nauseous.
Applications of Elevator Acceleration

Elevator acceleration has various practical applications, including:
- High-rise buildings: Elevators in high-rise buildings are designed to accelerate quickly to transport passengers to different floors efficiently.
- Amusement park rides: Some amusement park rides use elevators to accelerate passengers at high speeds for thrilling experiences.
Elevator acceleration can enhance the efficiency and safety of elevator systems by reducing travel time and providing a smoother ride.
Safety Considerations
There are several safety considerations related to elevator acceleration:
- Excessive acceleration: Too much acceleration can cause discomfort or injury to passengers.
- Sudden stops: Sudden stops can cause passengers to fall or collide with the walls of the elevator.
To ensure passenger safety, elevators are equipped with safety features such as speed limiters and emergency brakes to prevent excessive acceleration and sudden stops.
Future Developments
Advancements in technology could lead to even faster and more efficient elevators. For example, new materials and designs could reduce the weight of elevators, allowing for higher acceleration rates.
Additionally, improvements in control systems could enable elevators to accelerate and decelerate more smoothly, enhancing passenger comfort and safety.
Commonly Asked Questions: An Elevator Is Accelerating Upward 3.5 M/s2
What is the significance of upward acceleration in elevators?
Upward acceleration in elevators plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and speed of elevator systems, particularly in high-rise buildings. It allows elevators to reach higher floors more quickly, reducing waiting times and improving building accessibility.
How does acceleration affect passengers inside an elevator?
As an elevator accelerates upward, passengers experience a sensation of increased weight due to the inertial force acting upon them. This force pushes them against the elevator floor, creating a feeling of being pressed down. Additionally, the acceleration can cause slight disorientation and changes in balance.
What safety measures are in place to ensure passenger safety during elevator acceleration?
Elevator systems are equipped with various safety measures to ensure passenger safety during acceleration. These include:
- Speed governors: Devices that monitor the elevator’s speed and automatically engage if it exceeds a safe limit.
- Emergency brakes: Brakes that activate immediately to stop the elevator in case of an emergency.
- Buffer springs: Springs located at the bottom of the elevator shaft that absorb impact in the event of a sudden stop.