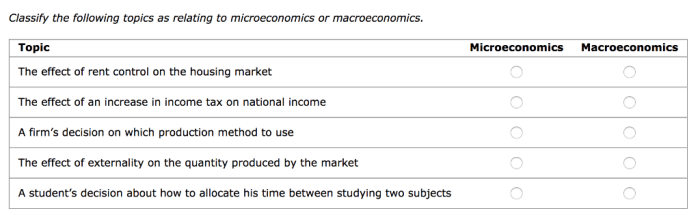
Classify the following topics as relating to microeconomics or macroeconomics. Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two broad branches of economics that examine different aspects of the economy. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual entities, such as consumers, firms, and industries, while macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including factors such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Understanding the distinction between microeconomics and macroeconomics is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals seeking to make informed economic decisions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and distinctions between these two fields of economics.
Microeconomics
Microeconomics examines the behavior of individual entities, such as consumers, firms, and industries, within the economy. It focuses on understanding how these entities interact and make decisions in specific markets.
Microeconomics has a significant impact on the overall functioning of the economy. It helps us understand how resources are allocated, prices are determined, and how markets function.
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are two fundamental concepts in microeconomics. Supply refers to the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price. Demand refers to the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price.
The interaction of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity of a good or service. When supply and demand are equal, the market is in equilibrium and the price is stable.
Elasticity
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of supply or demand to changes in price. Price elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a percentage change in price. Price elasticity of supply measures the percentage change in quantity supplied in response to a percentage change in price.
Elasticity is an important concept in microeconomics because it helps us understand how consumers and producers respond to changes in market conditions.
Government Intervention
Government intervention in microeconomic markets can take many forms, including price controls, subsidies, and taxes. The goal of government intervention is to correct market failures or to achieve specific policy objectives.
Government intervention can have a significant impact on the functioning of microeconomic markets. It can affect prices, quantities, and the distribution of income.
Market Structures
Market structures refer to the different types of markets that exist in an economy. The four main market structures are perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly.
Each market structure has its own unique characteristics that affect the behavior of firms and consumers.
| Market Structure | Number of Firms | Barriers to Entry | Price-Setting Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfect Competition | Many | None | None |
| Monopoly | One | High | Significant |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many | Low | Some |
| Oligopoly | Few | High | Significant |
Macroeconomics

Macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including the overall level of output, employment, and inflation. It focuses on understanding how these macroeconomic variables interact and how they are affected by government policies.
Macroeconomics has a significant impact on the lives of individuals and businesses. It helps us understand how economic growth occurs, how unemployment affects the economy, and how inflation can impact our purchasing power.
GDP
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a given period of time. It is the most widely used measure of economic output.
GDP is calculated by adding up the value of all final goods and services produced in the economy. Final goods and services are those that are sold to consumers or businesses for final use, rather than being used as inputs in the production of other goods and services.
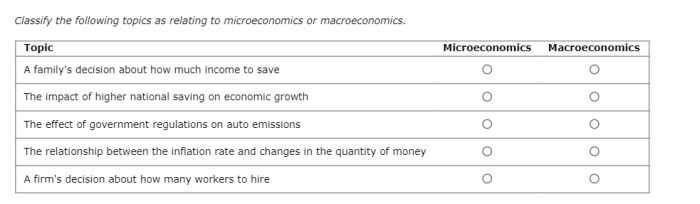
Monetary Policy, Classify the following topics as relating to microeconomics or macroeconomics
Monetary policy is the set of tools that the central bank uses to control the money supply and interest rates. The goal of monetary policy is to achieve specific macroeconomic objectives, such as price stability, economic growth, and full employment.
Monetary policy can have a significant impact on the economy. It can affect the level of investment, consumption, and economic growth.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. The goal of fiscal policy is to achieve specific macroeconomic objectives, such as stimulating economic growth, reducing unemployment, or controlling inflation.
Fiscal policy can have a significant impact on the economy. It can affect the level of aggregate demand, which is the total demand for goods and services in the economy.
Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policies
Expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending or reducing taxes in order to stimulate economic growth. Contractionary fiscal policy involves decreasing government spending or increasing taxes in order to reduce inflation.
The choice between expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies depends on the specific macroeconomic conditions that exist.
| Fiscal Policy | Government Spending | Taxes | Impact on Aggregate Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansionary | Increase | Decrease | Increase |
| Contractionary | Decrease | Increase | Decrease |
Interrelationship between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two closely related fields of economics. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual entities, while macroeconomics focuses on the economy as a whole.
Microeconomic factors can have a significant impact on macroeconomic outcomes. For example, changes in consumer spending can affect aggregate demand, which is the total demand for goods and services in the economy. Similarly, changes in business investment can affect economic growth.
Macroeconomic policies can also impact microeconomic behavior. For example, changes in interest rates can affect the investment decisions of businesses. Similarly, changes in government spending can affect the demand for goods and services produced by businesses.
It is important to understand both microeconomics and macroeconomics in order to make effective economic decisions. Microeconomics helps us understand how individual entities behave, while macroeconomics helps us understand how the economy as a whole functions.
| Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
|---|---|
| Focuses on individual entities | Focuses on the economy as a whole |
| Examines supply and demand, elasticity, and market structures | Examines GDP, monetary policy, and fiscal policy |
| Helps us understand how resources are allocated and prices are determined | Helps us understand how economic growth occurs and how unemployment and inflation affect the economy |
General Inquiries: Classify The Following Topics As Relating To Microeconomics Or Macroeconomics
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual entities within the economy, such as consumers, firms, and industries, while macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including factors such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Why is it important to understand both microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Understanding both microeconomics and macroeconomics provides a comprehensive perspective on the economy, enabling individuals and policymakers to make more informed decisions.
How can I apply microeconomic and macroeconomic principles in my daily life?
Microeconomic principles can help you understand consumer behavior and make informed purchasing decisions, while macroeconomic principles can provide insights into economic trends and policy implications.
