Introducing the solubility curve worksheet with answers, a valuable tool for understanding the intricacies of solubility and its dependence on temperature. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, factors influencing solubility, and its practical applications, making it an essential resource for students and professionals alike.
Delving into the world of solubility curves, we unravel the mysteries of saturation, the typical shape of these curves, and the profound impact of temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent on solubility. Through interactive elements and practice problems, this worksheet empowers learners to master the art of reading and interpreting solubility curves, extrapolating data, and applying their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Solubility Curve Worksheet: Overview: Solubility Curve Worksheet With Answers
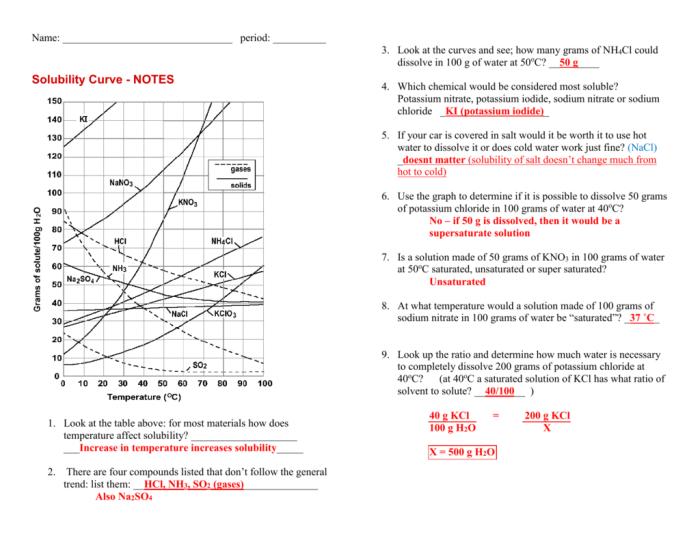
A solubility curve graphically represents the relationship between the solubility of a substance and temperature. It defines the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given solvent at a specific temperature, forming a saturated solution.
Saturation occurs when no more solute can be dissolved in the solvent at that temperature. The solubility curve helps predict the solubility of a substance at different temperatures.
Typically, a solubility curve slopes upward, indicating that solubility increases with increasing temperature. However, some substances exhibit retrograde solubility, where solubility decreases with increasing temperature.
Factors Affecting Solubility
- Temperature:Generally, solubility increases with increasing temperature. Higher temperatures provide more kinetic energy to solvent molecules, allowing them to break apart solute particles and dissolve them.
- Pressure:For gases, solubility increases with increasing pressure. Higher pressure forces more gas molecules into solution.
- Nature of solute and solvent:The chemical nature of the solute and solvent influences their interactions and, thus, solubility. Similar substances tend to be more soluble in each other (like dissolves like).
Reading and Interpreting Solubility Curves, Solubility curve worksheet with answers
To read a solubility curve:
- Locate the temperature on the x-axis and the solubility on the y-axis.
- Find the point where the temperature and solubility values intersect.
- The solubility at that temperature is indicated by the y-coordinate of the intersection point.
To extrapolate data from a solubility curve, extend the curve beyond the given data points to estimate solubility at other temperatures.
Applications of Solubility Curves
- Chemical engineering:Designing crystallization and extraction processes.
- Pharmaceutical formulations:Determining drug solubility and stability in different solvents.
- Environmental science:Predicting the solubility of pollutants in water and soil.
- Food science:Optimizing food processing and preservation techniques.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of a solubility curve?
A solubility curve graphically depicts the relationship between the solubility of a substance and temperature, providing insights into the temperature dependence of solubility.
How can I determine the solubility of a substance at a given temperature using a solubility curve?
Locate the corresponding temperature on the x-axis of the solubility curve and draw a vertical line to intersect the curve. The point of intersection on the y-axis indicates the solubility of the substance at that temperature.
What factors can affect the shape of a solubility curve?
The shape of a solubility curve can be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the solute and solvent, as well as the presence of impurities or other substances in the solution.