Unravel the mysteries of plant tropisms with our comprehensive Plant Tropisms Color by Number Answer Key. Embark on a captivating journey into the fascinating world of plant behavior, where light, gravity, and touch shape their growth and survival. This guide provides an illuminating exploration of the mechanisms, types, and real-world applications of plant tropisms, offering a profound understanding of these remarkable plant responses.
Delve into the intricacies of positive and negative phototropism, unravel the significance of geotropism for root growth, and discover the remarkable role of thigmotropism in plant support. Our meticulously designed color-coded table serves as the ultimate answer key for your plant tropisms color by number activity, providing a visual representation of the different tropism types and their corresponding colors.
1. Introduction
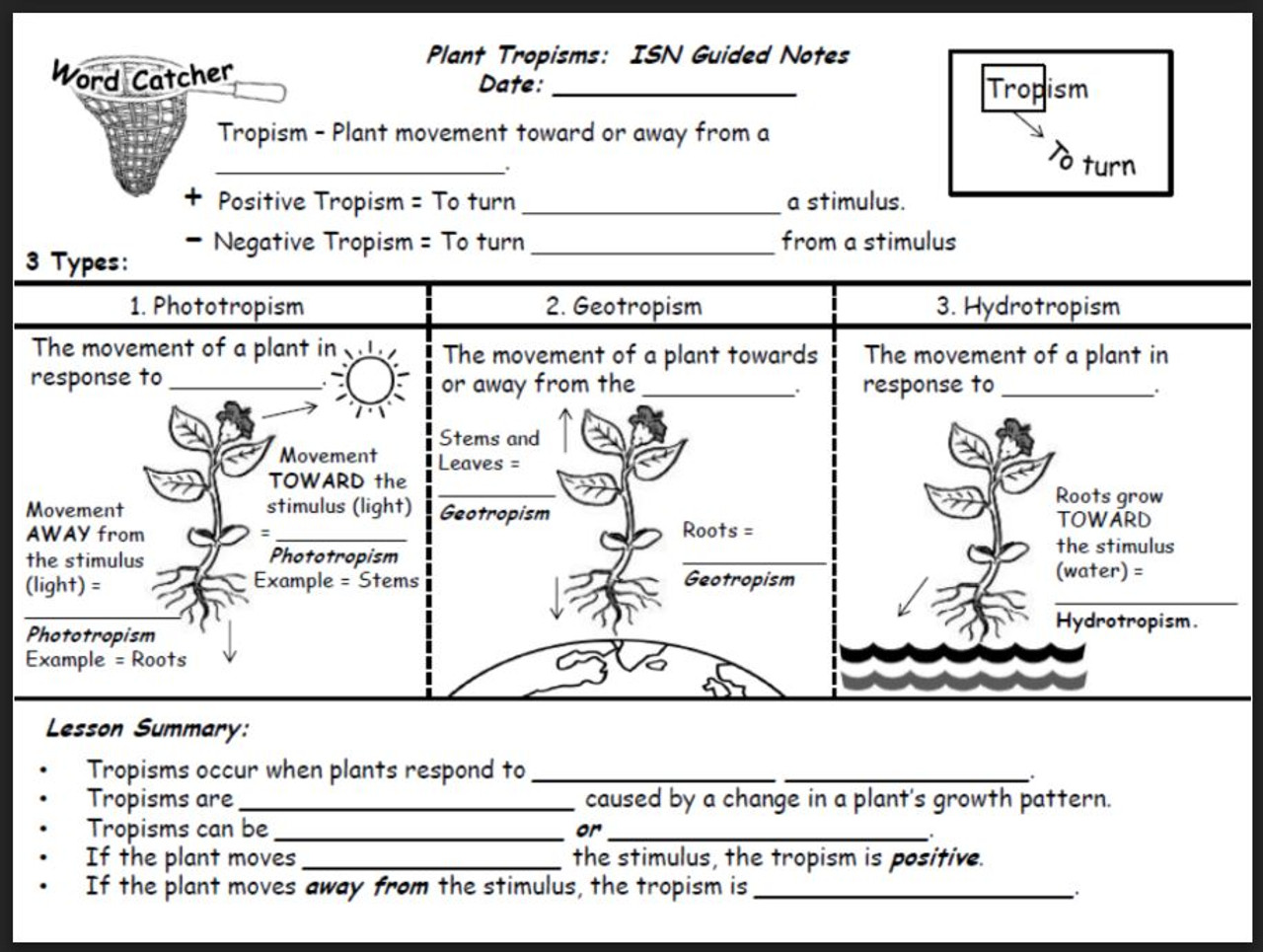
Plant tropisms are directional growth responses exhibited by plants in response to specific environmental stimuli. These responses play a crucial role in plant survival and growth, enabling them to optimize their orientation towards favorable conditions.
Light and other stimuli, such as gravity and touch, act as cues that trigger tropistic responses. These stimuli are detected by specialized receptors within plant cells, initiating a cascade of cellular and molecular events that lead to differential growth on specific sides of the plant, resulting in directional movement.
2. Types of Plant Tropisms: Plant Tropisms Color By Number Answer Key
2.1. Phototropism
Phototropism is the directional growth response of plants towards light. Positive phototropism refers to growth towards the light source, while negative phototropism indicates growth away from the light.
2.2. Geotropism
Geotropism is the growth response of plants in response to gravity. Positive geotropism, observed in roots, promotes downward growth, while negative geotropism, exhibited by shoots, results in upward growth.
2.3. Thigmotropism, Plant tropisms color by number answer key
Thigmotropism is the growth response of plants in response to touch or physical contact. Positive thigmotropism involves growth towards the stimulus, often observed in climbing plants, while negative thigmotropism refers to growth away from the stimulus.
3. Mechanism of Plant Tropisms
The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying plant tropisms are complex and involve various signaling pathways and hormonal responses.
Auxin, a plant hormone, plays a pivotal role in tropistic responses. Unequal distribution of auxin within the plant leads to differential cell elongation, resulting in the characteristic directional growth patterns observed in tropisms.
4. Color by Number Answer Key
| Color | Tropism Type |
|---|---|
| Red | Positive Phototropism |
| Blue | Negative Phototropism |
| Green | Positive Geotropism |
| Orange | Negative Geotropism |
| Yellow | Positive Thigmotropism |
| Purple | Negative Thigmotropism |
5. Examples of Plant Tropisms in Nature
Plant tropisms are evident in a wide range of plant species and habitats.
- Sunflowers exhibit positive phototropism, orienting their flower heads towards the sun for optimal photosynthesis.
- Roots of plants display positive geotropism, growing downward to anchor the plant and absorb nutrients from the soil.
- Tendrils of climbing plants exhibit positive thigmotropism, wrapping around supports to secure the plant’s growth.
6. Applications of Plant Tropisms
Understanding plant tropisms has practical applications in agriculture and horticulture.
- Manipulation of light conditions can optimize plant growth and productivity in greenhouses and indoor cultivation systems.
- Knowledge of geotropism helps in proper root development and transplantation techniques.
- Thigmotropism can be exploited in trellising and support systems for climbing plants.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of plant tropisms?
Plant tropisms play a crucial role in plant survival and growth. They enable plants to optimize their access to light, water, and nutrients, while avoiding harmful stimuli. Tropisms ensure proper root development, stem elongation, and leaf orientation, ultimately maximizing plant fitness and reproductive success.
How does light influence plant tropisms?
Light is a primary environmental cue that triggers phototropism in plants. Positive phototropism allows plants to orient their shoots towards light sources, maximizing photosynthesis and growth. Conversely, negative phototropism enables roots to grow away from light, ensuring proper anchorage and access to water and nutrients in the soil.
What are the practical applications of understanding plant tropisms?
Understanding plant tropisms has significant applications in agriculture and horticulture. By manipulating light and other environmental stimuli, growers can optimize plant growth, productivity, and quality. For example, controlled lighting in greenhouses can enhance crop yields, while trellising techniques utilize thigmotropism to support climbing plants.